Stethoscope
Leis stands at the forefront of innovation as a leading Stethoscope factory, revolutionizing the medical equipment industry on a global scale. Specializing in the export of premium medical stethoscope models, Leis has cultivated a reputation for excellence and precision. Our unwavering commitment to quality and customer satisfaction defines our operations, ensuring that healthcare professionals worldwide trust our products to perform under the most demanding conditions.
With a diverse range of offerings, our Deluxe Gold Plated CLASSIC II Stethoscope exemplifies the perfect fusion of sophistication and functionality. Each piece is crafted with a gold-plated stainless steel chestpiece and ear hook, complemented by a latex-free PVC tube available in a variety of colors to suit professional preferences and styles.
In an era where technology drives progress, our Bluetooth Digital Stethoscope leads the charge with its state-of-the-art wireless electronic model, facilitating seamless data transmission to both Android and iOS devices. This digital marvel, along with our Medical Digital Electronic Stethoscope, empowers healthcare providers with the ability to record and share auscultation data, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and consultation efficiency.
At Leis, we pride ourselves on delivering unparalleled value through high-quality, innovative medical stethoscope solutions, supported by a robust quality management system compliant with ISO13485 standards. Join us as we redefine excellence in medical diagnostics across the globe.
With a diverse range of offerings, our Deluxe Gold Plated CLASSIC II Stethoscope exemplifies the perfect fusion of sophistication and functionality. Each piece is crafted with a gold-plated stainless steel chestpiece and ear hook, complemented by a latex-free PVC tube available in a variety of colors to suit professional preferences and styles.
In an era where technology drives progress, our Bluetooth Digital Stethoscope leads the charge with its state-of-the-art wireless electronic model, facilitating seamless data transmission to both Android and iOS devices. This digital marvel, along with our Medical Digital Electronic Stethoscope, empowers healthcare providers with the ability to record and share auscultation data, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and consultation efficiency.
At Leis, we pride ourselves on delivering unparalleled value through high-quality, innovative medical stethoscope solutions, supported by a robust quality management system compliant with ISO13485 standards. Join us as we redefine excellence in medical diagnostics across the globe.
-
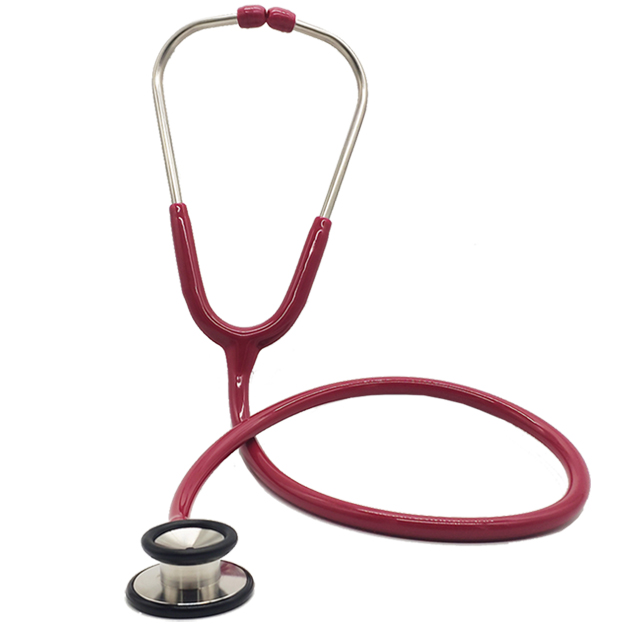

Medical Stainless Steel Cardiology Stethoscope
- Medical Stainless Steel Cardiology Stethoscope
- Double sided
- Stainless steel bell
- 47mm diameter of the head
- Stainless steel head material,PVC tube
-
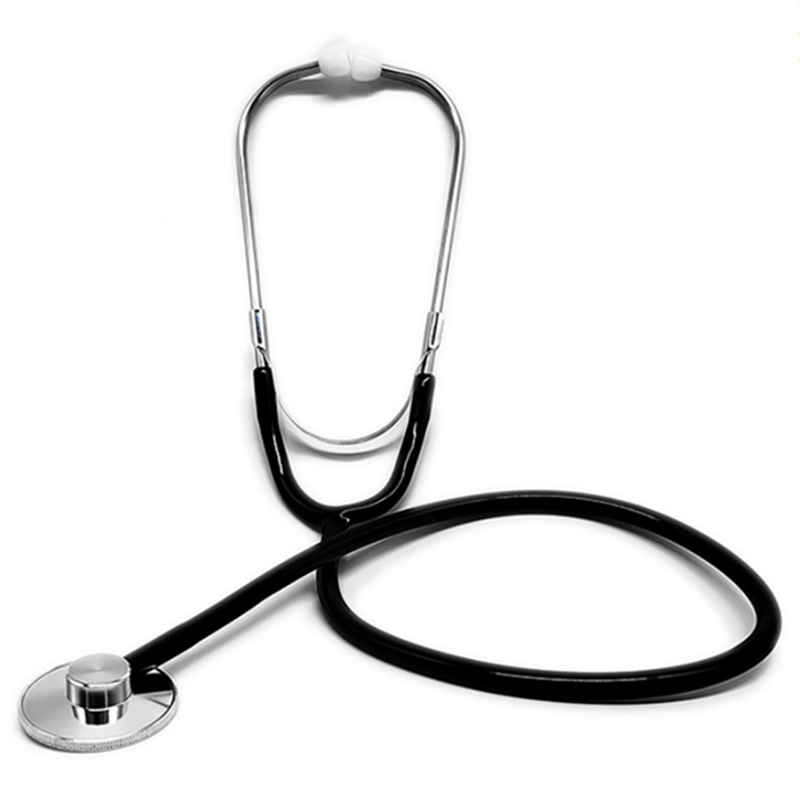
Single Head Aluminum Alloy Stethoscope
-
Single Head Stethoscope
- Aluminum Alloy bell
- Stainless steel earplug
- PVC tube
- Many colors for option
- Low cost,widely used
- Routine auscultation
-
The Frequent FAQs of Stethoscope
What is a stethoscope used for?▾
The stethoscope stands as an enduring emblem of the medical profession, symbolizing the bridge between doctor and patient. Its primary function extends beyond mere symbolism, serving as an essential tool for healthcare providers to listen to the internal sounds of the human body. This venerable instrument, often seen draped around the necks of doctors and nurses, facilitates the detection of critical health conditions through the amplification of body sounds, notably from the heart, lungs, and intestinal tract.
First invented in 1816, the stethoscope emerged from the necessity to conduct non-invasive examinations. Its original incarnation—a simple wooden tube—allowed physicians to listen to internal body sounds without direct physical contact with patients, which was often seen as intrusive. Over time, the medical stethoscope has undergone significant evolution, both in complexity and capability. Modern designs incorporate sound amplification and noise-canceling technologies, greatly enhancing a medical professional’s ability to discern and evaluate bodily functions accurately.
A contemporary medical stethoscope is composed of several key parts. The headset consists of ear tubes, tension springs, and ear tips, which are essential for transmitting sound from the patient to the healthcare provider. The chestpiece is the part placed against the patient’s skin, responsible for picking up sound vibrations. Inside the chestpiece, the diaphragm works to filter different frequency sounds, allowing physicians to isolate specific internal noises that can indicate various medical conditions.
The utility of the medical stethoscope is most apparent in its clinical applications. For cardiologists, it is an indispensable tool for detecting a range of heart-related abnormalities. By listening to the heart, a physician can identify conditions such as aortic stenosis, characterized by a narrowed valve, or valve leakage, recognized by abnormal blood flow sounds. Additionally, irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, can be detected using the stethoscope, providing critical information for diagnosing conditions like atrial fibrillation.
Beyond the heart, the medical stethoscope plays a crucial role in assessing lung health. Physicians listen for abnormal lung sounds, which might indicate respiratory conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis. Similarly, the stethoscope can be used to evaluate the intestinal tract, providing auditory clues to potential gastrointestinal issues. The ability to diagnose such a wide range of conditions underscores the stethoscope’s significance in preventive care and early intervention, which are pivotal in achieving better health outcomes.
The stethoscope continues to be a staple in the toolkit of healthcare professionals across the globe, despite advancements in diagnostic imaging technologies. Its non-invasive nature, immediate feedback, and ease of use make it an unparalleled diagnostic tool in both routine check-ups and emergency situations. With the integration of digital enhancements, modern stethoscopes now offer capabilities to store and analyze sound data, allowing for more detailed health monitoring and record-keeping.
In summary, the medical stethoscope is far more than a mere listening device. It is a powerful diagnostic tool that aids in the early detection and management of various health conditions, bridging the gap between clinical intuition and diagnostic precision. Its continued evolution and adaptability ensure its relevance in the future of medical care.
● The Evolution and Design of the Medical Stethoscope
First invented in 1816, the stethoscope emerged from the necessity to conduct non-invasive examinations. Its original incarnation—a simple wooden tube—allowed physicians to listen to internal body sounds without direct physical contact with patients, which was often seen as intrusive. Over time, the medical stethoscope has undergone significant evolution, both in complexity and capability. Modern designs incorporate sound amplification and noise-canceling technologies, greatly enhancing a medical professional’s ability to discern and evaluate bodily functions accurately.
○ Components of a Modern Stethoscope
A contemporary medical stethoscope is composed of several key parts. The headset consists of ear tubes, tension springs, and ear tips, which are essential for transmitting sound from the patient to the healthcare provider. The chestpiece is the part placed against the patient’s skin, responsible for picking up sound vibrations. Inside the chestpiece, the diaphragm works to filter different frequency sounds, allowing physicians to isolate specific internal noises that can indicate various medical conditions.
● Clinical Applications and Importance
The utility of the medical stethoscope is most apparent in its clinical applications. For cardiologists, it is an indispensable tool for detecting a range of heart-related abnormalities. By listening to the heart, a physician can identify conditions such as aortic stenosis, characterized by a narrowed valve, or valve leakage, recognized by abnormal blood flow sounds. Additionally, irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, can be detected using the stethoscope, providing critical information for diagnosing conditions like atrial fibrillation.
○ Diagnosing Lung and Abdominal Conditions
Beyond the heart, the medical stethoscope plays a crucial role in assessing lung health. Physicians listen for abnormal lung sounds, which might indicate respiratory conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis. Similarly, the stethoscope can be used to evaluate the intestinal tract, providing auditory clues to potential gastrointestinal issues. The ability to diagnose such a wide range of conditions underscores the stethoscope’s significance in preventive care and early intervention, which are pivotal in achieving better health outcomes.
● The Stethoscope in Modern Healthcare
The stethoscope continues to be a staple in the toolkit of healthcare professionals across the globe, despite advancements in diagnostic imaging technologies. Its non-invasive nature, immediate feedback, and ease of use make it an unparalleled diagnostic tool in both routine check-ups and emergency situations. With the integration of digital enhancements, modern stethoscopes now offer capabilities to store and analyze sound data, allowing for more detailed health monitoring and record-keeping.
In summary, the medical stethoscope is far more than a mere listening device. It is a powerful diagnostic tool that aids in the early detection and management of various health conditions, bridging the gap between clinical intuition and diagnostic precision. Its continued evolution and adaptability ensure its relevance in the future of medical care.
Can a stethoscope detect lung problems?▾
The stethoscope, an enduring symbol of medical practice, plays a crucial role in assessing lung health. For decades, healthcare professionals have relied on this simple yet effective tool to detect a range of lung problems, from common respiratory infections to more serious conditions. Through a process called auscultation, doctors use the stethoscope to listen to the sounds produced within the lungs, providing essential clues about a patient’s respiratory status.
Breath sounds, as heard through a medical stethoscope, are the acoustic signals produced by the movement of air through the respiratory tract. These sounds can be heard in various parts of the chest, including above the collarbones and at the base of the rib cage. During auscultation, a clinician may identify normal, abnormal, or absent breath sounds, each of which can offer insight into underlying lung conditions.
Normal lung sounds indicate healthy airflow, whereas deviations from this can point to potential issues. Abnormal breath sounds, often categorized into rales, rhonchi, stridor, and wheezing, can signal various conditions. Rales, for example, are characterized by clicking or rattling noises, often an indication of air opening closed spaces within the lungs. These sounds can be moist, dry, fine, or coarse, providing further diagnostic clues. Rhonchi resemble snoring and occur when airflow is obstructed in the large airways, while stridor, a wheeze-like sound, suggests a blockage in the trachea or throat. Wheezing, typically heard during exhalation, indicates narrowed airways, commonly associated with asthma or bronchitis.
The presence of abnormal breath sounds, as detected through a stethoscope, can be indicative of several lung conditions. These include acute and chronic bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, emphysema, and interstitial lung disease, among others. Additionally, conditions such as congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema can present with characteristic breath sounds that guide further medical evaluation and intervention.
While the medical stethoscope is invaluable for initial assessments, its findings are often supplemented by other diagnostic tools to confirm the nature and extent of lung problems. Blood tests, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests provide comprehensive insights into respiratory health. These tests help in corroborating the auscultatory findings, ensuring a precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Prompt medical evaluation is critical when abnormal breath sounds are detected. Symptoms like severe shortness of breath, cyanosis, or nasal flaring warrant immediate attention. In such cases, the healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination and inquire about the patient’s medical history and symptoms. This comprehensive approach ensures that the underlying cause of abnormal breath sounds is accurately identified and effectively managed.
In conclusion, the stethoscope remains an indispensable tool in the detection of lung problems. While it provides essential preliminary insights into respiratory health, its findings are often part of a larger diagnostic framework. The marriage of traditional auscultation with modern diagnostic technologies continues to enhance our ability to identify and treat lung conditions effectively, ensuring better patient outcomes.
● The Mechanics of Lung Sounds
Breath sounds, as heard through a medical stethoscope, are the acoustic signals produced by the movement of air through the respiratory tract. These sounds can be heard in various parts of the chest, including above the collarbones and at the base of the rib cage. During auscultation, a clinician may identify normal, abnormal, or absent breath sounds, each of which can offer insight into underlying lung conditions.
○ Normal and Abnormal Breath Sounds
Normal lung sounds indicate healthy airflow, whereas deviations from this can point to potential issues. Abnormal breath sounds, often categorized into rales, rhonchi, stridor, and wheezing, can signal various conditions. Rales, for example, are characterized by clicking or rattling noises, often an indication of air opening closed spaces within the lungs. These sounds can be moist, dry, fine, or coarse, providing further diagnostic clues. Rhonchi resemble snoring and occur when airflow is obstructed in the large airways, while stridor, a wheeze-like sound, suggests a blockage in the trachea or throat. Wheezing, typically heard during exhalation, indicates narrowed airways, commonly associated with asthma or bronchitis.
● Diagnostic Implications
The presence of abnormal breath sounds, as detected through a stethoscope, can be indicative of several lung conditions. These include acute and chronic bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, emphysema, and interstitial lung disease, among others. Additionally, conditions such as congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema can present with characteristic breath sounds that guide further medical evaluation and intervention.
○ The Role of Complementary Diagnostics
While the medical stethoscope is invaluable for initial assessments, its findings are often supplemented by other diagnostic tools to confirm the nature and extent of lung problems. Blood tests, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests provide comprehensive insights into respiratory health. These tests help in corroborating the auscultatory findings, ensuring a precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
● Seeking Medical Attention
Prompt medical evaluation is critical when abnormal breath sounds are detected. Symptoms like severe shortness of breath, cyanosis, or nasal flaring warrant immediate attention. In such cases, the healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination and inquire about the patient’s medical history and symptoms. This comprehensive approach ensures that the underlying cause of abnormal breath sounds is accurately identified and effectively managed.
In conclusion, the stethoscope remains an indispensable tool in the detection of lung problems. While it provides essential preliminary insights into respiratory health, its findings are often part of a larger diagnostic framework. The marriage of traditional auscultation with modern diagnostic technologies continues to enhance our ability to identify and treat lung conditions effectively, ensuring better patient outcomes.
